reMARBL3D
at TIME SPACE EXISTENCE, Venice, 2023
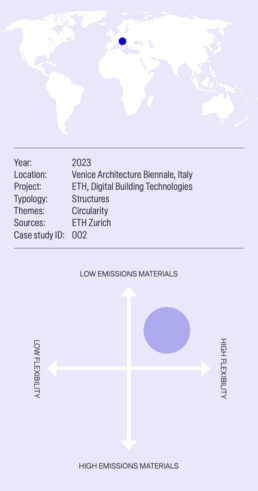
Researchers at ETH Zurich and SUPSI’s Institute of Earth Sciences have developed a dry-assembled funicular floor composed of 17 blocks 3D printed with recycled marble aggregates – approximately 80% of the printed material.
This 3D printing process enables the manufacture of large-scale components suitable for structural applications using byproducts of stone extraction.
The disposal of construction and quarry waste poses a significant environmental challenge, with up to 40% of this waste ending up in landfill. By transforming this waste into valuable construction products, the research addresses both waste management and the need for new materials.
The 3D printing method used is Binder Jetting (BJT), which uses a two-component binder system. A granular base is combined with an activating liquid alkali solution, which is sprayed through nozzles in layers, resulting in durable printed parts with excellent mechanical properties and resistance to weather and fire.



Related Posts
16/06/2025
ECOALF STORE
16/06/2025
RADICANT
16/06/2025
3D PRINTED FILM STUDIO
16/06/2025
InNoFa-DEMONSTRATOR
16/06/2025
THE WAVE HOUSE
16/06/2025
STRESS-BASED DESIGN
16/06/2025
TIFFANY FAÇADE
16/06/2025
CERAMIC HOUSE
16/06/2025
WOHN HOMES
16/06/2025
THE EGGSHELL PROJECT
16/06/2025
3DNATURDRUCK
16/06/2025
TO GROW A BUILDING
16/06/2025
TECLA
16/06/2025
REEFCIRCULAR
16/06/2025
AIRLEMENTS
16/06/2025
TOVA
16/06/2025
HIVE Project
16/06/2025


















